Hello Readers,
Formulas play an important role in solving various maths problems. Because of its importance, Here we provide a chapter-wise list of formulas for class 8th.
Rational Numbers
⇒ The rational number 0 is the additive identity for rational numbers.
⇒ The rational number 1 is the multiplicative identity for rational numbers.
Understanding Quadrilaterals
⇒ The sum of all interior angles of a Polygon = 180(n-2)
⇒ The sum of all the exterior angles of Polygon = 360°
⇒ The sum of all the interior angles of the Triangle = 180°
⇒ The sum of all the interior angles of the Quadrilateral = 360°
⇒ Exterior angle of Regular Polygon = 360°/No. of Sides
⇒ No. of sides of Regular Polygon = 360°/Exterior Angle
⇒ Exterior Angle = 180° - Interior Angle
⇒ The minimum interior angle possible for a regular polygon = 60°.
⇒ The maximum exterior angle possible for a regular polygon = 120°.
⇒ Perimeter of parallelogram = Sum of all sides.
⇒ The sum of any two adjacent angles of Parallelogram = 180°
⇒ The sum of all the interior angles of the Parallelogram = 360°
Data Handling
⇒ Total angle at the center of a circle = 360°.
⇒ Probability = (No. of favorable Outcomes of an event)/(Total no. of Outcomes)
Squares and Square roots
⇒ All square numbers end with 0, 1, 4, 5, 6, or 9 at unit place.
⇒ To find the numbers that lie between the squares of two consecutive numbers = 2n
⇒ To Find the square of the number-
(a+b)²=a²+2ab+b²
(a-b)²=a²-2ab+b²
⇒ Pythagorean Triplet:- 2m, m²-1, m²+1
⇒ Area of square = Side×Side
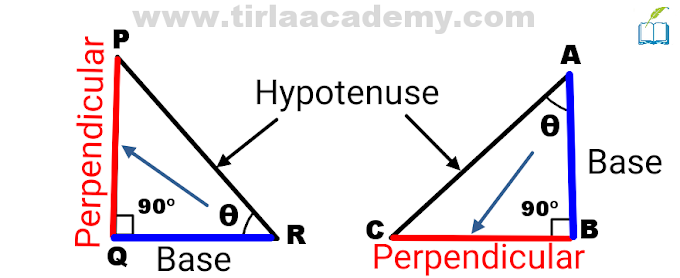
⇒ Pythagoras Theorem:- H² = P² + B²
Cubes and Cube roots
⇒ Volume of Cuboid = Length×Breadth×Height
⇒ The volume of Cube = (Length of side)³
Comparing Quantities
⇒ 1km = 100m
⇒ 1Rs. = 100paise
⇒ Discount = Marked Price - Sale Price
⇒ Discount % = (Discount price×100)/Marked Price
⇒ Simple Interest = (P×R×T)/100
⇒ Amount = Principal + Interest
⇒ Amount = Principal×[1+(Rate/100)]ⁿ
⇒ Compound Interest = Amount - Principal
Algebraic Expressions and Identities
⇒ Area of Rectangle = Length × Breadth
⇒ The volume of the Rectangular Box = Length×Breadth×Height
⇒ (a+b)(a-b)=a²-b²
Mensuration
⇒ Area of Triangle = 1/2×b×h
⇒ Area of Trapezium = h/2×(a+b)
⇒ Area of Quadrilateral = D/2(H₁+H₂)
⇒ Area of Rhombus = 1/2×D₁×D₂
⇒ Area of Rectangle = Length × Breadth
⇒ Area of Square = Side×Side
⇒ Total Surface Area of Cube = 6×(Length of side)²
⇒ Lateral Surface Area of Cube = 4×(Length of side)²
⇒ Total Surface Area of Cuboid = 2(lb+bh+hl)
⇒ Lateral Surface Area of Cuboid = 2(bh+hl)
⇒ Total Surface Area of Cylinder = 2𝜋r(r+h)
⇒ Curved Surface Area of Cylinder = 2𝜋rh
⇒ Volume of Cube = (Length of side)³
⇒ Volume of Cuboid = Length×Breadth×Height
⇒ Height of Cuboid = Volume of Cuboid/Base Area
⇒ Volume of Cylinder = 𝜋r²h
⇒ 1 Litre = 1000cm³
⇒ 1 m³ = 1000 Litre
⇒ 1 m³ = 1000000cm³
⇒ 1ml = 1cm³
⇒ 1m = 100cm
Exponents and Powers
⇒ a-ᵐ = 1/aᵐ
⇒ aᵐ×aⁿ=aᵐ⁺ⁿ
⇒ aᵐ÷aⁿ=aᵐ⁻ⁿ
⇒ (aᵐ)ⁿ=aᵐⁿ
⇒ aᵐ×bᵐ=(ab)ᵐ
⇒ aᵐ÷bᵐ=(a÷b)ᵐ
⇒ a° = 1
Direct and Inverse Proportions
⇒ Direct Proportion x₁/y₁ = x₂/y₂
⇒ Inverse Proportion x₁y₁ = x₂y₂
Factorisation
⇒ (a+b)²=a²+2ab+b²
⇒ (a-b)²=a²-2ab+b²
⇒ (a+b)(a-b)=a²-b²
⇒ (x+a)(x+b)=x²+(a+b)x+ab